| tense | Affirmative/Negative/Question | Use | Signal Words |
|---|
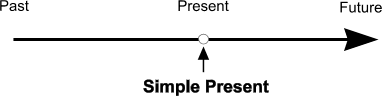
| Simple Present | A: He speaks.
N: He does not speak.
Q: Does he speak? |
- action in the present taking place regularly, never or several times
- facts
- actions taking place one after another
- action set by a timetable or schedule
| always, every …, never, normally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually
if sentences type I (If Italk, …) |
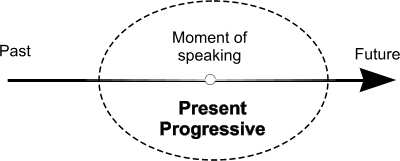
| Present Progressive | A: He is speaking.
N: He is not speaking.
Q: Is he speaking? |
- action taking place in the moment of speaking
- action taking place only for a limited period of time
- action arranged for the future
| at the moment, just, just now, Listen!, Look!, now, right now |
| Simple Past | A: He spoke.
N: He did not speak.
Q: Did he speak? |
- action in the past taking place once, never or several times
- actions taking place one after another
- action taking place in the middle of another action
| yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the other day, last Friday
if sentence type II (If Italked, …) |
| Past Progressive | A: He was speaking.
N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking? |
- action going on at a certain time in the past
- actions taking place at the same time
- action in the past that is interrupted by another action
| while, as long as |
| Present Perfect Simple | A: He has spoken.
N: He has not spoken.
Q: Has he spoken? |
- putting emphasis on the result
- action that is still going on
- action that stopped recently
- finished action that has an influence on the present
- action that has taken place once, never or several times before the moment of speaking
| already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now |
| Present Perfect Progressive | A: He has been speaking.
N: He has not been speaking.
Q: Has he been speaking? |
- putting emphasis on the course or duration (not the result)
- action that recently stopped or is still going on
- finished action that influenced the present
| all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?, the whole week |
| Past Perfect Simple | A: He had spoken.
N: He had not spoken.
Q: Had he spoken? |
- action taking place before a certain time in the past
- sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive
- putting emphasis only on the fact (not the duration)
| already, just, never, not yet, once, until that day
if sentence type III (If Ihad talked, …) |
| Past Perfect Progressive | A: He had been speaking.
N: He had not been speaking.
Q: Had he been speaking? |
- action taking place before a certain time in the past
- sometimes interchangeable with past perfect simple
- putting emphasis on the duration or course of an action
| for, since, the whole day, all day |
| Future I Simple | A: He will speak.
N: He will not speak.
Q: Will he speak? |
- action in the future that cannot be influenced
- spontaneous decision
- assumption with regard to the future
| in a year, next …, tomorrow
If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her, she will help you.)
assumption: I think, probably, perhaps |
| Future I Simple
(going to)
| A: He is going to speak.
N: He is not going to speak.
Q: Is he going to speak? |
- decision made for the future
- conclusion with regard to the future
| in one year, next week, tomorrow |
| Future I Progressive | A: He will be speaking.
N: He will not be speaking.
Q: Will he be speaking? |
- action that is going on at a certain time in the future
- action that is sure to happen in the near future
| in one year, next week, tomorrow |
| Future II Simple | A: He will have spoken.
N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken? |
- action that will be finished at a certain time in the future
| by Monday, in a week |
| Future II Progressive | A: He will have been speaking.
N: He will not have been speaking.
Q: Will he have been speaking? |
- action taking place before a certain time in the future
- putting emphasis on the courseof an action
| for …, the last couple of hours, all day long |
| Conditional I Simple | A: He would speak.
N: He would not speak.
Q: Would he speak? |
- action that might take place
| if sentences type II
(If I were you, I would go home.) |
| Conditional I Progressive | A: He would be speaking.
N: He would not be speaking.
Q: Would he be speaking? |
- action that might take place
- putting emphasis on the course/ duration of the action
| |
| Conditional II Simple | A: He would have spoken.
N: He would not have spoken.
Q: Would he have spoken? |
- action that might have taken place in the past
| if sentences type III
(If I had seen that, Iwould have helped.) |
| Conditional II Progressive | A: He would have been speaking.
N: He would not have been speaking.
Q: Would he have been speaking? |
- action that might have taken place in the past
- puts emphasis on the course / duration of the action
| |